A. Arithmetic Array
Solution:
For the sum less than n, we just need append one number to make the sum equal to n.
For the sum more than n, we append some zero to make n equal to the sum.
Code:
Java

C++

B. Bad Boy
Solution:
No matter where the initial position is, the result must be two opposite corners. So, just print 1 1 n m.
Code:
Java

C++

C. Challenging Cliffs
Solution:
After sort by the height. Two adjacent numbers with the smallest difference can be selected as one head and one tail.
To have the highest cost, it is necessary to keep the array single increment as much as possible. So, we can do something below:
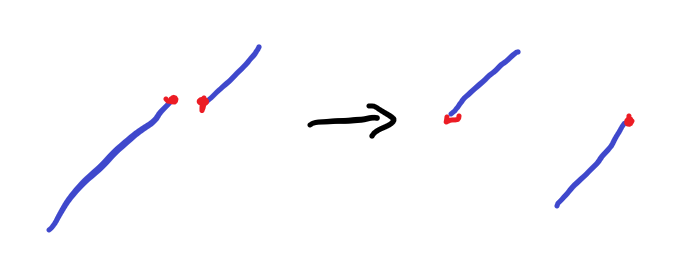
Code:
Java

C++

D. Deleting Divisors
The breakthrough is the initial value is odd. Because the odd number only can be transfer to even number. Then we separate the initial value to 3 categories, and just find the status transition.
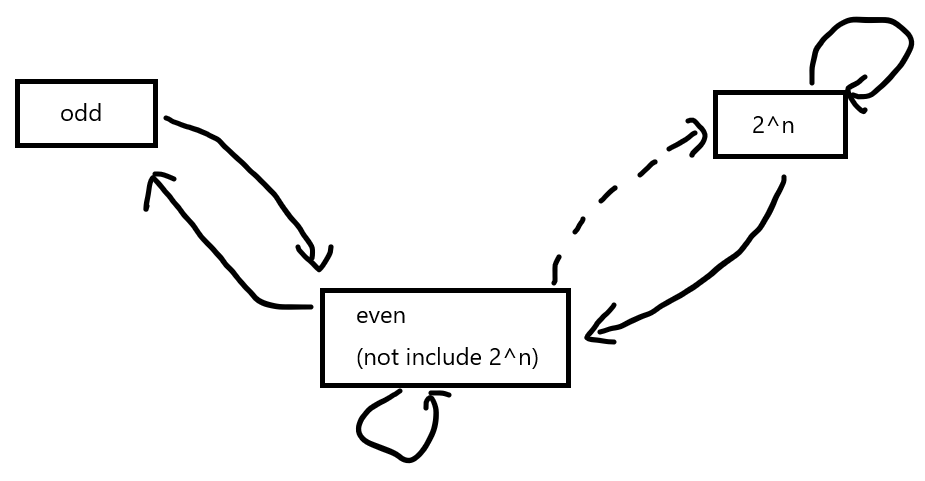
I am too tired these few days. Even problem E and F lower than 2500. But I do it later.
